Discover Florida Nature
It's time to explore the natural Florida


|
|
|
|
|
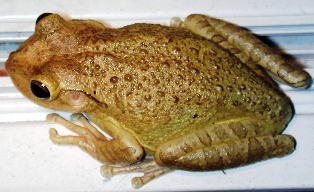 Cuban
Treefrog- Cuban Treefrogs are now abundant in the state of
Florida, although when first introduced, they were limited to the
Florida Keys and the Miami-Dade area. Spreading rapidly through both
south and central Florida, the Cuban Treefrog readily eats the smaller
native frogs. After a rainy night, these frogs often call intensely in
the wee hours of the morning until just before sunrise. Their call is a
drawn-out nasal sound, usually repeated two or three times. Cuban
treefrogs can change colors quickly from light gray to dark brown. This
frog seems to be a favorite snack for many native snakes, including the
garter snake and the
hognose. Cuban
Treefrog- Cuban Treefrogs are now abundant in the state of
Florida, although when first introduced, they were limited to the
Florida Keys and the Miami-Dade area. Spreading rapidly through both
south and central Florida, the Cuban Treefrog readily eats the smaller
native frogs. After a rainy night, these frogs often call intensely in
the wee hours of the morning until just before sunrise. Their call is a
drawn-out nasal sound, usually repeated two or three times. Cuban
treefrogs can change colors quickly from light gray to dark brown. This
frog seems to be a favorite snack for many native snakes, including the
garter snake and the
hognose. Green
Treefrog- The Green Treefrog is probably the most familiar
treefrog in the state of Florida. This treefrog is common, fairly large,
and it adapts to living near homes where it can search for food around
windows and under outdoor lights at night. The Green Treefrog, or
Cow-bell Frog, as it is sometimes called has a call that sounds like a
ringing bell like sound. A chorus of many males together is nothing
short of mind boggling, since each one of perhaps a hundred frogs might
be calling at a slightly different pitch. Green Treefrogs breed in
water that is several feet deep in permanent ponds, instead of the
shallow temporary ponds that most other Florida frogs use. Usually vivid
green, the Green Treefrog can change to brown quickly. The well defined
strip that runs the length of its side makes identifying the Green
Treefrog easy. Green
Treefrog- The Green Treefrog is probably the most familiar
treefrog in the state of Florida. This treefrog is common, fairly large,
and it adapts to living near homes where it can search for food around
windows and under outdoor lights at night. The Green Treefrog, or
Cow-bell Frog, as it is sometimes called has a call that sounds like a
ringing bell like sound. A chorus of many males together is nothing
short of mind boggling, since each one of perhaps a hundred frogs might
be calling at a slightly different pitch. Green Treefrogs breed in
water that is several feet deep in permanent ponds, instead of the
shallow temporary ponds that most other Florida frogs use. Usually vivid
green, the Green Treefrog can change to brown quickly. The well defined
strip that runs the length of its side makes identifying the Green
Treefrog easy. Squirrel
Treefrog- The squirrel treefrog is highly variable in color and
pattern, and may at any time be colored green, brown, or green and
brown, and may be spotted or plain. Sometimes a dark spot or bar may
appear between its eyes. A light stripe might also occur on the sides of
its body. Its common name, "Squirrel Treefrog," comes from its scolding,
squirrel-like raspy call, often emitted during rain storms. Generally,
the squirrel treefrog prefers habitats that are moist, provide shade,
and where its preferred food source of insects are abundant. As their
name suggests, treefrogs are well adapted to life in an arboreal
environment. Their toes have adhesive disks that allow them to climb
easily on bark or twigs. Treefrogs are usually found in habitats such as
wet hammocks, marshes, mixed hardwood swamps, and cypress swamps. Squirrel
Treefrog- The squirrel treefrog is highly variable in color and
pattern, and may at any time be colored green, brown, or green and
brown, and may be spotted or plain. Sometimes a dark spot or bar may
appear between its eyes. A light stripe might also occur on the sides of
its body. Its common name, "Squirrel Treefrog," comes from its scolding,
squirrel-like raspy call, often emitted during rain storms. Generally,
the squirrel treefrog prefers habitats that are moist, provide shade,
and where its preferred food source of insects are abundant. As their
name suggests, treefrogs are well adapted to life in an arboreal
environment. Their toes have adhesive disks that allow them to climb
easily on bark or twigs. Treefrogs are usually found in habitats such as
wet hammocks, marshes, mixed hardwood swamps, and cypress swamps. Gray
Treefrog- The Gray Treefrog's back is usually two-toned gray
with a broad patch of darker gray at the center. However, it also has
the ability to blend into its surroundings by changing colors from
green, brown or white. It can be distinguished from other treefrogs by
the bright yellow or orange of the inner thighs. The Gray Treefrog is
found in northern Florida, as far down as Marion County in Florida. It
lives in damp habitats, open parks, farmlands and cypress heads. Most of
the time it can be found in trees or shrubs growing in or near water.
The call of the Gray Treefrog lasts up to ten seconds and is a coarse,
resonant trill. Gray
Treefrog- The Gray Treefrog's back is usually two-toned gray
with a broad patch of darker gray at the center. However, it also has
the ability to blend into its surroundings by changing colors from
green, brown or white. It can be distinguished from other treefrogs by
the bright yellow or orange of the inner thighs. The Gray Treefrog is
found in northern Florida, as far down as Marion County in Florida. It
lives in damp habitats, open parks, farmlands and cypress heads. Most of
the time it can be found in trees or shrubs growing in or near water.
The call of the Gray Treefrog lasts up to ten seconds and is a coarse,
resonant trill. Barking
Treefrog- The barking treefrog is so named because of it nine
or ten syllable bark-like call. The barking treefrog is one of the
larger, most stout and more spotted of all the tree frogs. Its coloring
varies from dark brown, bright green, or pale yellow or grey, although
some green coloring is evident throughout all color phases. It ranges in
size from 2 to 2 5/8 inches. The Barking Treefrog can be found in sandy
areas in pine savannas and in low wet woods and swamps. When inactive
during cold or dry seasons, the barking treefrog burrows under tree
roots, vegetation, or in soil. This frog is otherwise mostly arboreal
and thus dependent on trees near water. Barking
Treefrog- The barking treefrog is so named because of it nine
or ten syllable bark-like call. The barking treefrog is one of the
larger, most stout and more spotted of all the tree frogs. Its coloring
varies from dark brown, bright green, or pale yellow or grey, although
some green coloring is evident throughout all color phases. It ranges in
size from 2 to 2 5/8 inches. The Barking Treefrog can be found in sandy
areas in pine savannas and in low wet woods and swamps. When inactive
during cold or dry seasons, the barking treefrog burrows under tree
roots, vegetation, or in soil. This frog is otherwise mostly arboreal
and thus dependent on trees near water. Pinewoods
Treefrog- The pine woods treefrog is similar in appearance to
the squirrel treefrog, except that it has a row of small orange, yellow,
or even whitish spots on the rear of the thigh that cannot be seen when
the frog is at rest. This frog's toes are only slightly webbed, and it
often breeds in temporary wetlands, including roadside ditches. The
habitat of treefrogs includes moist wooded, swamps, and brushy areas.
The Pinewoods Treefrog can be found in pine flatwoods, as well as
marshes. As their name suggests, tree frogs are well adapted to life in
an arboreal environment. Their toes have adhesive disks that allow them
to climb easily on bark or twigs. The sporadic chattering call of the
pine woods treefrog gives it the nickname "Morse-code frog." It can be
heard from April to October. Pinewoods
Treefrog- The pine woods treefrog is similar in appearance to
the squirrel treefrog, except that it has a row of small orange, yellow,
or even whitish spots on the rear of the thigh that cannot be seen when
the frog is at rest. This frog's toes are only slightly webbed, and it
often breeds in temporary wetlands, including roadside ditches. The
habitat of treefrogs includes moist wooded, swamps, and brushy areas.
The Pinewoods Treefrog can be found in pine flatwoods, as well as
marshes. As their name suggests, tree frogs are well adapted to life in
an arboreal environment. Their toes have adhesive disks that allow them
to climb easily on bark or twigs. The sporadic chattering call of the
pine woods treefrog gives it the nickname "Morse-code frog." It can be
heard from April to October.
|
|
|
Advertise | Privacy Statement | Dog Encyclopedia | Video |Contact | Alaska Nature |
|